Delve into the realm of private health insurance for self-employed business owners, where the right coverage can make all the difference. This introductory passage sets the stage for a comprehensive exploration of a crucial topic that impacts many entrepreneurs.
The following paragraph will provide detailed insights and information about the subject matter.
Overview of Private Health Insurance for Self-Employed Business Owners
Private health insurance for self-employed individuals refers to health coverage purchased by individuals who work for themselves or run their own businesses. Unlike traditional employer-sponsored health insurance, self-employed business owners are responsible for obtaining their own health insurance coverage.Having private health insurance as a self-employed business owner is crucial for ensuring access to quality healthcare services without facing financial hardships.
It provides coverage for medical expenses, preventive care, and treatments for illnesses or injuries, offering peace of mind and security in times of need.
Benefits of Private Health Insurance
- Customizable Coverage: Private health insurance plans can be tailored to meet individual needs, including specific medical services, prescriptions, and preferred healthcare providers.
- Greater Control: Self-employed individuals have more control over their healthcare choices, such as selecting doctors, hospitals, and treatment options.
- Portability: Private health insurance is not tied to a specific employer, allowing self-employed business owners to maintain coverage regardless of job changes.
- Enhanced Benefits: Private plans may offer additional benefits like wellness programs, dental and vision coverage, and alternative therapies not typically covered by other health insurance options.
Statistics on Private Health Insurance for Self-Employed Individuals
According to recent data, approximately [insert percentage] of self-employed individuals in the United States have private health insurance coverage. This highlights the importance of private health insurance in providing self-employed business owners with essential healthcare protection and financial security.
Considerations When Choosing Private Health Insurance
When selecting a private health insurance plan as a self-employed business owner, there are several factors to consider to ensure you get the coverage that meets your needs and budget.
Types of Private Health Insurance Plans
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): Requires you to choose a primary care physician and get referrals to see specialists.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): Offers more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers but at a higher cost.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): Similar to a PPO but with a more limited network of providers.
- High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP): Lower monthly premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs before insurance kicks in.
Coverage Options in Private Health Insurance Plans
- Doctor visits and specialist consultations
- Hospital stays and surgeries
- Prescription drug coverage
- Mental health services
- Maternity and newborn care
- Preventive care and wellness programs
Cost Analysis and Budgeting
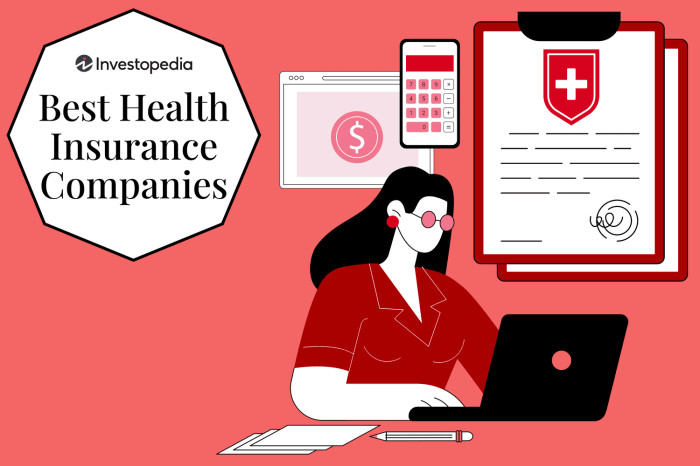
As a self-employed business owner, budgeting for private health insurance premiums is crucial to ensure you have adequate coverage without overspending. Here are some strategies to help you manage costs effectively while maintaining the coverage you need.
Strategies for Budgeting
- Calculate your monthly income and expenses to determine how much you can allocate towards health insurance premiums.
- Consider opting for a higher deductible plan to lower your monthly premiums, but make sure you have enough savings to cover the deductible in case of emergencies.
- Look for health insurance plans specifically designed for self-employed individuals, as they may offer more affordable options tailored to your needs.
Reducing Costs while Maintaining Coverage
- Compare different insurance providers to find the best rates and coverage options that fit your budget.
- Consider joining a professional organization or association that offers group health insurance plans for self-employed individuals at discounted rates.
- Explore health savings accounts (HSAs) or flexible spending accounts (FSAs) to save money on healthcare expenses with pre-tax dollars.
Tax Deductions and Credits
- Self-employed individuals may be eligible to deduct a portion of their health insurance premiums as a business expense on their tax return.
- Depending on your income level, you may qualify for tax credits through the Health Insurance Marketplace to help offset the cost of private health insurance.
- Consult with a tax professional to ensure you are taking advantage of all available deductions and credits related to private health insurance as a self-employed business owner.
Enrollment Process and Eligibility

When it comes to enrolling in a private health insurance plan as a self-employed business owner, there are specific steps you need to follow along with eligibility criteria that you must meet. Understanding these aspects is crucial to ensure you get the coverage you need.
Enrollment Process
- Research Different Plans: Start by researching different private health insurance plans available in your area. Look into their coverage, network of providers, and costs.
- Choose a Plan: Once you've compared your options, select a plan that best fits your needs and budget.
- Submit an Application: Fill out the necessary paperwork and submit your application for the chosen health insurance plan.
- Payment: After your application is approved, make sure to pay your premiums on time to activate your coverage.
Eligibility Criteria
- Self-Employed Status: You must be a self-employed individual, such as a freelancer, contractor, or business owner, to qualify for private health insurance as a self-employed person.
- Income Requirements: Some private health insurance plans may have income requirements that you need to meet to be eligible for coverage.
- No Access to Employer-sponsored Insurance: You should not have access to employer-sponsored health insurance through a spouse or any other means to be eligible for private health insurance as a self-employed individual.
Special Consideration: Self-employed individuals may be eligible for certain tax deductions related to their health insurance premiums. Consult with a tax professional to explore these options.
Managing Health Insurance as a Self-Employed Professional
When you are a self-employed business owner, managing your private health insurance effectively is crucial to ensure you have coverage when you need it most. It's important to stay on top of your health needs and be prepared for any changes that may impact your coverage.
The Importance of Regular Health Check-ups and Preventive Care
Regular health check-ups and preventive care are essential for self-employed individuals with private health insurance. By staying proactive with your health, you can catch any potential issues early on and prevent more serious health concerns down the line. It's also a way to make the most out of your insurance plan by utilizing preventive services that are often covered at no additional cost.
- Make sure to schedule regular check-ups with your primary care physician to monitor your overall health.
- Take advantage of preventive services such as vaccinations, screenings, and counseling to maintain your well-being.
- Stay informed about your insurance plan's coverage for preventive care to maximize its benefits.
Handling Changes in Income or Circumstances
As a self-employed professional, your income and circumstances may fluctuate, which can affect your private health insurance coverage. It's essential to know what to do in case of changes to ensure you have the right level of coverage when you need it.
Keep your insurance provider informed about any changes in your income or circumstances that may impact your coverage eligibility.
- Explore options for adjusting your insurance plan based on your current needs and budget.
- Consider switching to a different plan or provider if your current coverage is no longer suitable for your situation.
- Consult with a healthcare insurance advisor to help you navigate changes and make informed decisions about your coverage.
Wrap-Up
Concluding our discussion on private health insurance for self-employed business owners, this final section encapsulates key points and leaves readers with a lasting impression of the importance of securing the right coverage.
Key Questions Answered
What factors should self-employed business owners consider when choosing a private health insurance plan?
Self-employed individuals should consider factors such as coverage options, premiums, deductibles, network of providers, and any additional benefits offered in the plan. It's important to choose a plan that aligns with your healthcare needs and budget.
Are there tax deductions or credits available for self-employed individuals with private health insurance?
Yes, self-employed individuals may be eligible for tax deductions on their health insurance premiums. Additionally, they might qualify for tax credits under certain circumstances. It's advisable to consult with a tax professional to maximize these benefits.
How can self-employed business owners effectively manage their private health insurance coverage?
To manage their coverage effectively, self-employed individuals should review their plan regularly, stay informed about any changes in benefits or costs, utilize preventive care services, and be proactive in addressing any issues that may arise with their insurance provider.